Welcome to the second blog in our Viruses and Malware series – today, we’re looking at Trojans and Ransomware.
What are Trojans?
- Named after the Trojan Horse from the Greek myths, this type of malware works in a very similar way. Here’s an example:
-
- You receive an email containing a PDF document about horses and a gift from your enemy who has apparently decided to forgive and forgot! That’s great because you love PDFs about horses!
- You download the attachment.
- But that PDF document about horses actually contained malware and your computer has now been infected!
- Really easy right? So it’s not surprising that this is the most common way computers become infected.
- Especially if the attachment or download is from a site or emailer you trust. The payloads of Trojans vary greatly as the label Trojan only describes how the malware gets onto your machine – not what its goal is.
Payload: what the malware’s purpose is (a.k.a the way it messes with your computer).
Common malware spread through Trojans
- Ransomware
- Ransomware is a type of malware that takes your data hostage by threatening to delete it, permanently encrypt it or publish it unless a ransom is paid. The ransom is normally in bitcoin or another cryptocurrency as they are harder for authorities to track.
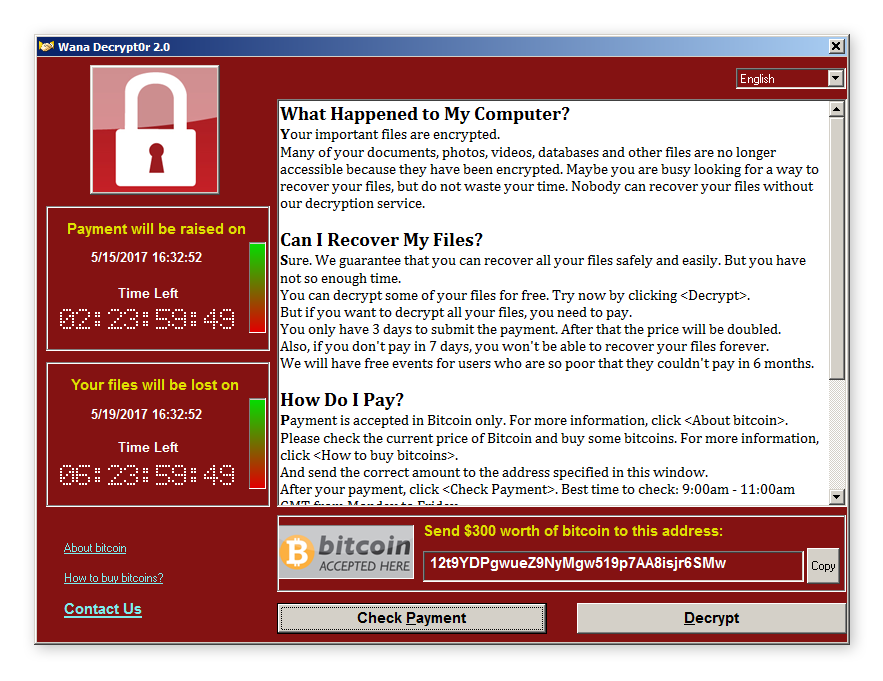
-
- They are commonly carried out using a Trojan – but the famous Ransomware WannaCry that attacked the NHS amongst other businesses, universities, and governments in 2017 was actually spread by a worm! Find out more about worms here.
- The number of ransomware attacks grows year on year, affecting both business and home users.
- Backdoors
- Although Trojans’ payloads can be anything, most modern forms act as a backdoor to a user’s computer.
- A backdoor allows unauthorised access to the device – giving the attacker access to personal information such as banking information, passwords, or personal identity without you knowing.
- Botnets
- Botnets are a group of infected computers that can do the dirty work of criminals such as denial of service attacks on a website, creating false traffic on a website, or even mining for bitcoin.
Worried your home or business isn’t well enough protected against the threat of malware? We can help – give us a call on 01553 692727 to talk to one of our engineers and find out how we can help!
